Japanese multinational conglomerate Hitachi is going big on the Internet-of-Things (IoT), robotics and artificial intelligence (AI), which the firm believes could push business further, improve productivity, reduce costs and improves people’s lives.
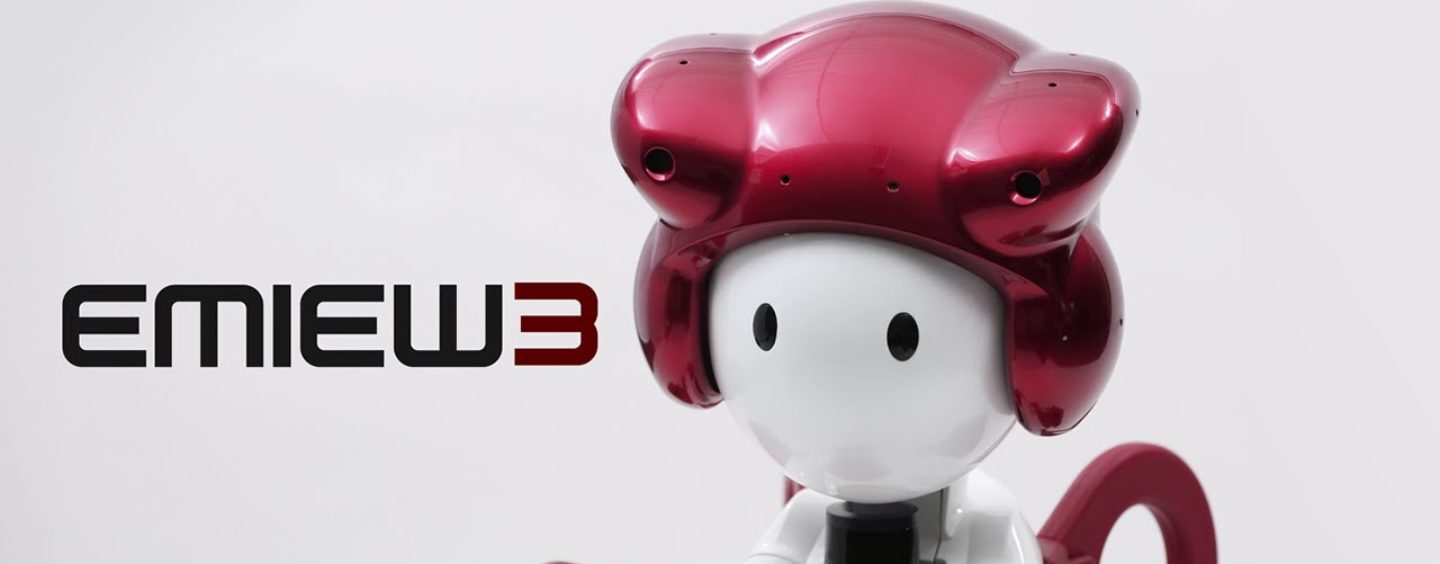
The EMIEW3 robot
Hitachi has developed the robotics IT platform and the humanoid robot EMIEW3 that can support humans’ daily activities by its independent action from thinking for itself.

Hitachi researchers: YAMAMOTO Akihiro, ASANO Yu, TOKUHASHI Kazumasa, and MATSUDA Tomohiro, via Hitachi
Unlike most robots which are used in industries, EMIEW3’s purpose is to live with humans and assist us in our daily lives, serving as a reliable helper in such situations, responding to any question with a broad as well as deep knowledge of its assigned territory.
EMIEW3’s technical capabilities include interacting with people through speech, and moving at the same pace as humans to guide people to targeted locations. Through active-learning dialogue data-based AI, EMIEW3 can learn about information that may change frequently, such as flight status, and correctly respond to customer enquiries.
Possible areas of application include increasingly sophisticated services for people, such as passenger guidance in facilities such as airports and stations, requiring multiple language services, customer support in outlets handling various complicated services, such as banks, and assistance to older persons or children – users who may not be familiar with information services.
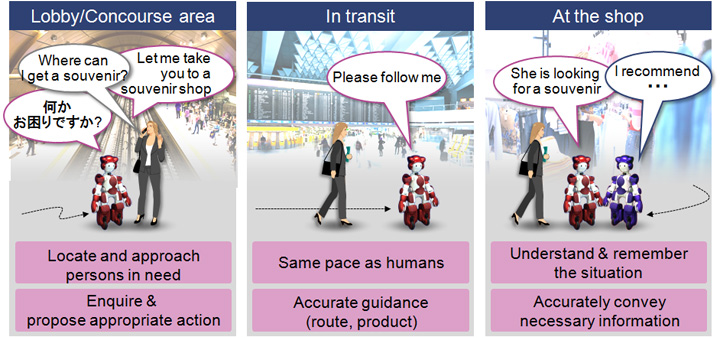
EMIEW3 is composed of a robot body and a computer system with cloud. The team designed an external application platform on cloud for voice recognition, location detection, language processing and so on, keeping only the essential functions requiring real-time response such as collision avoidance running in the robot.
The platform is called the “robotics IT platform” and allows the robot to have a smaller and lighter body which can behave responding to voice recognition result and realize accurate movements.
It also enables Hitachi to easily extend EMIEW3’s functions by connecting with other business systems and knowledge databases, such as those from customers.
In September 2016, Hitachi started trials of its EMIEW3 robot at Tokyo’s Haneda airport to aid foreign visitors in Japan.
Hitachi’s social innovation business
Hitachi’s robotics are a part of the firm’s expanding global social innovation business, which aims to create novel solutions to social challenges.
But Hitachi Group’s robotics activities can be traced back to the 60s with its Servo-Manipulator, a remote controlled device for nuclear power plant operations. Since then, the firm has introduced a wide variety of robots, and in 2005, it became the first companies to develop a human symbiotic robot. EMIEW3 was introduced in 2016.
Further marking its commitment to advance IoT, data center, cloud and analytics, Hitachi launched Hitachi Vantara in September 2017, an entity that unifies a series of enterprise units including Hitachi Data Systems, Hitachi Insight Group, and Pentaho.
At Hitachi’s Social Innovation Forum 2017 held in London in late November 2017, Ram Ramachander, chief digital officer and chief commercial officer of Hitachi’s social innovation business division in EMEA & CIS, said:
“Social innovation advances society; it aims to solve fundamental problems. […] Social innovation [is] possible now in a way we have never seen before.
Social innovation is coming into Asean..
Ref : https://www.hitachi.com.sg/press/press_2017/20170912.html