Li Wangjian, CEO of UQPAY: Blockchain Technology Is Reshaping Supply Chain Finance
by Li Wangjian, CEO of UQPAY May 21, 2018The concept of blockchain emerged in 2016 and was popularized in the latter half of 2017, along with the rapid rise of bitcoin, and then declined due to the crackdowns on ICO and virtual digital currency trading by the Central Bank at the turn of 2017-2018. In one year or so, virtual digital currencies stole the spotlight, and attracted a large amount of capital and aroused plenty of attention.
In contrast, the blockchain was buried in oblivion. In fact, over the past year, the blockchain circle has been drilling diligently and has widely applied blockchain in the industry, with lots of excellent applications and cases in cross-border payment, insurance, notarization, medical treatment and the transaction of intellectual property rights, especially in the field of supply chain finance.
Supply chain finance has always been the focus of the industry. On the one hand, China, as a big manufacturing country, its capital flow attains unprecedented scale,with tens of trillion yuan’s worth of accounts receivable and negotiable instruments flow in the domestic market each year.
On the other hand, the innovation in the field of supply chain finance is of great significance to the deleverage and the “Made in China 2025” strategy. With the characteristics of decentralized, trustfree and natural settlement, the blockchain technology has solved the problems of information asymmetry, absence of trusted center, and complex payment and settlement, showing unprecedented vitality in this field.
The status quo of supply chain finance
Supply chain is an organic combination of logistics, capital flow and information flow, of course, the concept of business flow was added in them later. Traditionally, these three flows have their corresponding service providers and their integration also has a large number of mature plans, but the ultimate goal of all these basic work is to serve supply chain finance and solve its problems such as financing costs, capital utilization rate, etc.
As far as suppliers are concerned, long payment days and high financing costs are both factors that constrain their development and expanded reproduction, and tight capital chain may even bring them to the edge of bankruptcy; money is not a problem for the core enterprises, instead, how to use these money more efficiently to produce benefits is a major task.
Meanwhile, core enterprises also pay special attention to controlling upstream suppliers firmly so as to gain an advantageous position in industry competition; banks focus on careful supervision to ensure that the information is true and effective, and the financing risk is manageable.
With the development of technology and the opening-up of the financial market, supply chain finance has demonstrated great vitality and new characteristics, for example, intensified competition among banks after the marketization of interest rates, the development of factoring and P2P businesses diversifying fund providers, and the development of the Internet and the Internet of Things greatly improving the efficiency of information circulation.
However, there still exist problems. For example, accounts receivable, different from negotiable instruments, are difficult to circulate, with high cost in pledge financing; the credit standing of core enterprises cannot be transmitted to tier-two or tier-three suppliers, causing the failure of financing among these suppliers in the supply chain, and the vexed issues of false warehouse receipts and repeated pledging, and so on.
However, the emergence of blockchain provides a perfect solution for the industry. Blockchain + supply chain marks a new start.
Technical characteristics of blockchain
Take a brief look at what the blockchain has brought to us. The Blockchain is not a new technology, but a technology integrating and utilizing point-to-point communication, encryption algorithm and other existing technologies, which, has brought profound changes and far-reaching influence to our life.
Above all, the blockchain provides a trusted network dispensing with a third party center:
- For all the transaction information, nodes are temporarily selected and recorded by the blockchain network, without the involvement of a third party center or the control of individuals and organizations.
- The data of all nodes are synchronized in real time, so the failure of a single node does not affect the whole system.
- All transactions are signed, therefore cannot be falsified by others.
These advantages are very attractive, which are also the reasons why the blockchain technology has raised concerns of the industry. However, there are still many problems at the beginning of the emergence of public blockchain.
- High consumption of resources. Random brute-force calculation costs a lot of computer resources and power, so that large quantities of electricity generated worldwide are consumed in this field.
- Low accounting efficiency. The other problem of random brute-force calculation is to exert strict control over the difficulty in the calculation of random numbers, which should not be too difficult to solve, or else it will be unavailable to users and the transactions will be difficult to record; while it cannot be too simple, otherwise, many people are easy to obtain a number that meets the requirements at the same time, so that there will be more than one person in the blockchain keeping accounts separately, thus resulting in bifurcation. Therefore, an equilibrium point is found, which, in turn, results in very low accounting efficiency of bitcoins. A block is generated every 7 minutes or so, and only 7 transactions are recorded per second. In addition, there is very small probability that many people keep accounts at the same time, leading to the bifurcation of the blockchain, which will be eventually solved by abandoning a bifurcation, so that all transactions of the abandoned bifurcation will be invalidated, thereby causing huge losses.
- 51% attack. Once someone controls more than 51% computing power of the entire network, it will be able to run faster than others, thereby controlling the bifurcation of the block and attacking abandoned bifurcation.
The technology, with these defects, cannot be applied in the industry, so the industry has made improvements, especially in consensus mechanism.
As significant differences exist between the industry application and bitcoin, the bookkeeping nodes of the blockchain are wh borne by everyone, they are, however, generally the responsibility of a few big agencies, just like giants in a consortium, thus giving rise to the concept of the Consortium Blockchain. Consortium Blockchain distinguishes blockchain from bitcoin, a fully open public blockchain.
The consensus mechanism of the Consortium Blockchain only needs to be agreed by several members, and does not need to determine a bookkeeper by the way of calculating the random number.
The bookkeeper of the next block can be exclusively and effectively determined through voting and rotation and a variety of ways, which thoroughly resolves the problems existing in bitcoin network, such as resource consumption, bifurcation and 51% attack, making it possible for the commercialization of blockchain technology to become a reality.
How does the blockchain change supply chain finance?
- A typical case of traditional supply chain finance
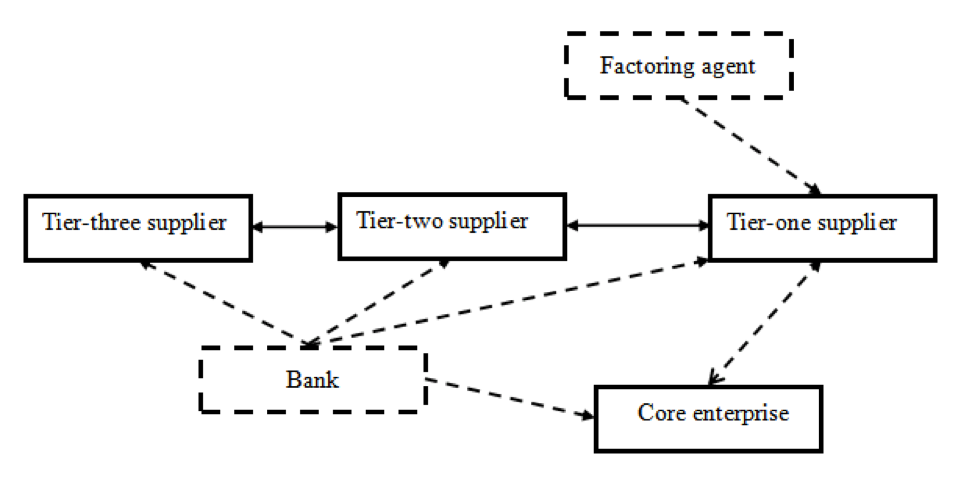
Take the supply chains of core manufacturing enterprises as an example. According to usual practices of the traditional model:
- Accounts receivable are incurred between core enterprises and tier-one suppliers, and between tier-one and tier-two suppliers.
- Banks grant a large number of credits to core enterprises, but are very cautious about granting credits to tier-one suppliers, and hardly provide credits to tier-two or tier-three suppliers.
Then when a tier-one supplier is lack of purchasing funds, it has several options available, first is to seek financing from core enterprises, second is to raise funds from banks with its accounts receivable as pledge, and third is to apply for the factoring of accounts receivable.
However, it is difficult for a tier-two supplier to raise funds, as it is unable to seek financing from core enterprises, and difficult to raise financing from banks by relying on the accounts receivable between it and tier-one supplier, or apply for the factoring of accounts receivable, not mentioning tier-three suppliers.
- Main problems existing in the traditional supply chain finance
In fact, main problems of supply chain finance at this stage include:
- Accounts receivable cannot directly circulate. As guaranteed by the credit standing of a core enterprise, a tier-one supplier may raise funds by relying on accounts receivable incurred between it and the core enterprise. Therefore, a tier-one supplier may finance in this way, but it is difficult to transmit the raised funds to enterprises in upstream chain, as tier-two and tier-three suppliers cannot utilize the credit standing of the core enterprise, thus being difficult to finance.
- High cost of financing. Short term funds acquired by suppliers with accounts receivable as pledge are high in financing costs, as the funds occupy risk measurement capitals and raise the leverage of banks.
- Unfavorable credit environment. Loan fraud by false warehouse receipts is very common in the pledging of warehouse receipts, therefore each link is lack of authenticity and reliability.
- Difficulty for a third party to intervene in this business. Because of the lack of reliable credit standing, a third party is struggling between supply chain financial services dominated by banks and core enterprises, and do not have the advantage either in capitals or in upstream and downstream industry chain.
To sum up, all the problems are actually due to the lack of trust. Because core enterprises do not trust tier-two and tier-three suppliers as they trust tier-one suppliers, so small and medium-scale suppliers in upstream chain are difficult to obtain financing, even if they obtain financing, the cost is very high.
In addition, due to the lack of trust and supervision mechanism, the authenticity of business data cannot be guaranteed, resulting in frequent occurrence of crimes; finally, the lack of credit standing which is trusted by supply chain participants makes a third party more difficult to succeed in supply chain financing.
- Changes brought by the blockchain
The blockchain features a decentralized trust mechanism, which is the most appropriate technology to solve the pain points in the field of supply chain finance.
If all participants are placed in the blockchain (as shown below), and all nodes share the same information, all above-mentioned problems will be easily solved.
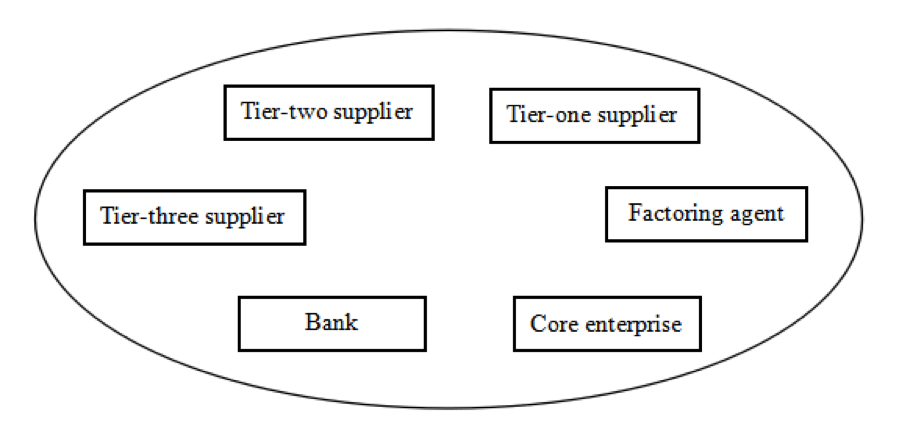
- Divisible and negotiable accounts receivable. Accounts receivable should be deposited in supply chain in the form of digital assets, to convert the accounts receivable incurred between core enterprises and tier-one suppliers into digital assets, which can be divided, transferred and traced.Tier-one suppliers can use the digital assets as a payment tool, and divide and pay them to tier-two suppliers, so that tier-three suppliers will receive digital assets which can be traced back to the credits of core enterprises, with values significantly higher than that received by tier-one suppliers in the traditional mode. Even if the assets are indefinitely passed on, they are always guaranteed by the credit standing of the core enterprises.
- To reduce the cost of financing. Once the accounts receivable can be circulated and paid, the enterprises in the blockchain can make a payment by such digital assets to solve payment problems, and they no longer need to seek pledge financing, but only need to pay the confirmation commission.
- To solve the problem of the difficulty in financing. When small and medium-scale suppliers make a payment to enterprises outside of the blockchain by digital assets which are converted from accounts receivable and are guaranteed by the credit standing of core enterprise, they will easily get more capitals from banks and factoring agents, so as to thoroughly solve the problems of difficult financing.
- Deleverage. On the one hand, the leverage of enterprises is reduced, and on the other hand, less risk capitals of banks are occupied, which is totally consistent with the “deleverage” strategy that the whole society advocates.
- To provide the operation capability of a third party except banks and core enterprises. Since the blockchain ensures the data not to be tampered, it is completely different from the traditional centralization mode that all participants worry about the tampering of the data by a third party operator.
This model ensures the trustworthiness of the data, guaranteeing the feasibility of the third party operation, which is not possible in the traditional mode.
Consideration on investing assets in supply chain
It is a matter of concern how to invest the assets in the supply chain among the three modes of supply chain finance: accounts receivable financing, prepayments financing, personal estate financing.
The most distinct feature of the transaction in the chain of bitcoin is that the value transfer is completed with the transaction closing. Whereas it is different in the supply chain finance that accounts receivable, prepayments and personal estate are all existing off the chain, without corresponding assets in the blockchain, and cannot be conducted credible transaction and transfer directly in the chain. Therefore, digital twin or other means are necessary for the association of physics-digital world.
Comparatively, it is easier to apply the blockchain on accounts receivable and prepayments for both the two types of assets can be digitized naturally. The receiving and paying parties can fully record and confirm respective accounts receivable and prepayments in the chain, so as to form valid in-chain contract, and subsequent assets of this kind absolutely can flow in the chain unrestrictedly.
When there is need of financing, the investor can implement the subsequent steps just after verifying the authenticity of trade, which completely meets the conditions of in-chain digital transaction.
Unlike the accounts that can be digitized and homogenized, personal estate financing is open to changes. As material objects, with various specifications, qualities and conditions, the personal estate is hardly accurately evaluated and validated, which is also the reason for the frequent occurrence of the cases such as loan fraud by false warehouse receipts.
Even if the pledge of personal estate completed in the chain is legally transferred and circulated in the chain, once pledge right preservation occurs, the real value will come from the possession of objects from the physical world, rather than the chain. Only if the authenticity and value of the objects are guaranteed can this be accomplished.
Currently, there are plenty of schemes trying to achieve the binding of physical objects from the real world and the assets in the chain, but no effective method appears now. Actually, this problem had already existed before the blockchain came into being, but blockchain itself cannot solve the problem either, only when the Internet of Thing develops, and techniques mature in information acquisition, evaluation, monitoring and control of physical object, can an indeed effective method be put forward.
Summary and outlook
To sum up, we can see that, different from some applications in other fields that make up something unnecessary and even a lot of pseudo demands, the application of the blockchain to the supply chain finance is automatic and natural. The characteristics of the blockchain completely solve the existing shortages and problems in supply chain finance, and even have a positive effect on the “deleveraging” policy at the national level.
Furthermore, in addition to the great function performed in domestic supply chain finance, applying the blockchain technology is more helpful in building technical rigidity guaranteed trust mechanism under complicated circumstances since trust relationship, supervision pattern and capital control is rather complicated in cross-border supply chain finance than those in the domestic environment.
Meanwhile, an unobstructed circulation mechanism for cross-border values can be provided through the expedite circulation of digital currency. Under this circumstance, we affirm that blockchain owns a broader application value and prospect.
Featured image via Pixabay







