
Digital Payments Transformation: Changing How Business Gets Done
by Fintech News Singapore April 26, 2021The trend toward payments digitisation is undeniable. Worldwide, transaction value of digital payments is expected to reach USD 8.7 trillion by 2025. In China alone, arguably the biggest market in the world in digital payments, transaction value has already hit $1.6 trillion in 2019.
The implications of the shift to digital payments in the consumer and business-to-business (B2B) marketplaces are significant.
However, adoption of digital payments technology varies widely across the Asia Pacific region. In Singapore, debit and credit cards represent 65 percent of e-commerce transactions. In India, cash still represents approximately 96 percent of total payment transaction volume while China has adapted well to the trend with strong digital payments adoption in both the consumer and B2B markets.
The migration from cash to digital payments has been building momentum for years as a result of new technology, consumer demand, fintech disruption and regulatory initiatives. In 2020, the global pandemic sent this transformation into hyperdrive with the growth of e-commerce as businesses and consumers made more purchases online. This digital environment has given rise to new types of payment service providers that have begun to challenge banks as the primary provider of digital payments and related services.
For an in-depth look at factors shaping the payments transformation, download the Accuity whitepaper, Digital Payments: Is This Really Goodbye to Cash? An Analysis of Business and Consumer Trends.
Consumers Lead While B2B Follows
With widespread internet access and smartphone use, consumers quickly embraced the convenience of digital payments. Their experience and expectation of fast, frictionless transactions have, in turn, shaped expectations in the B2B sector. Additionally, an estimated two billion unbanked and underbanked individuals worldwide now rely on the fast, secure and inexpensive methods that mobile payments offer.
Consequently, companies now expect their financial service providers to deliver the same frictionless process and payment choices available to consumers. This includes more payment products and options across a broader swath of geographies, along with quicker settlement times and lower fees.
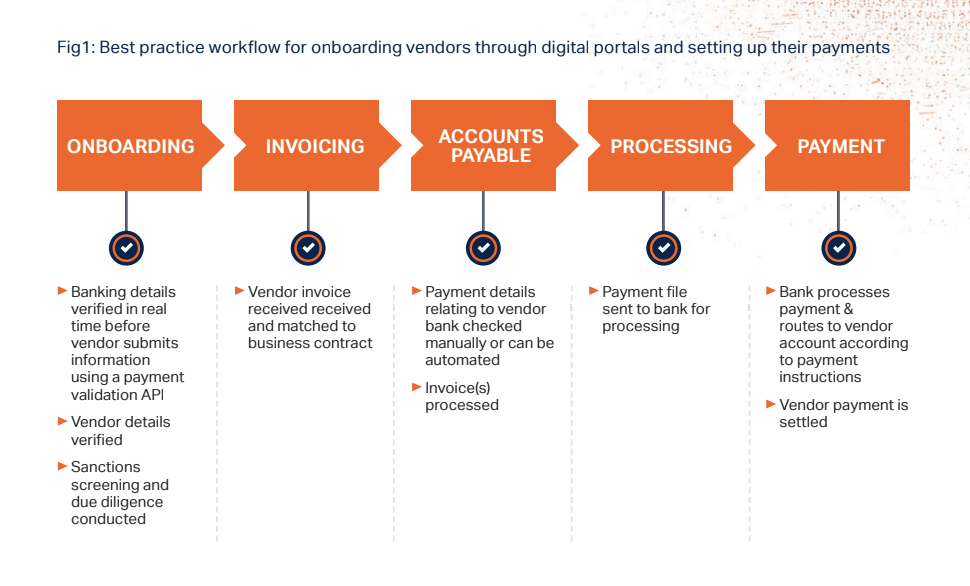
As payments become increasingly electronic in the B2B environment, organisations can amplify the benefits of transformation by updating overall processes to remove friction, increase speed, lower costs, and improve efficiency. This requires a holistic approach that addresses the entire workflow starting at onboarding and continuing through payments processing and reconciliation.
The Benefits of Payments Digitisation for the Corporate Sector
Payments digitisation creates some obvious opportunities by improving payment options and customer experience. However, organisations must have the right infrastructure to support new technology. That often requires a reengineering and different way of thinking about workflow, processes and payments.
Organisations would be best served by integrating technology into an existing ecosystem to overcome logistical barriers that exist in their payment processes. Reengineered processes will also lead to better compliance and improvements in onboarding, KYC, payment reconciliation, and straight-through processing rates.
Source: Accuity’s whitepaper Digital Payments: Is This Really Goodbye to Cash? An Analysis of Business and Consumer Trends
Better access to data will also provide more visibility and predictability in the payments process allowing for transparency into inbound and outbound payment flows as well as better customer information. This greater insight into customer behaviour will enable more targeted product and service offerings enhancing customer satisfaction and leading to greater engagement.
The Impact to Financial Institutions
In Europe, open banking initiatives have completely changed the landscape for financial institutions (FIs), driving up competition from challenger banks and other innovative payments providers. To embrace transformation, FIs must be able to deliver solutions and processes that can scale and that evolve quickly. This level of agility and flexibility is not at the core of how traditional institutions operate, which has compelled FIs to work more closely with fintech companies and PSPs to fill the gap.
Consumers, organisations and FIs all stand to benefit as electronic payment methods increase as a percentage of accounts payable payments.
The Growing Influence of Fintechs and Non-Banks
The introduction of new banking standards and regulatory initiatives, such as Financial Planning Digital Services in Singapore have opened the door to third parties like fintechs and non-banks to handle financial transactions. Newer, more nimble providers like Ant Group and Sea, which were just awarded digital bank licenses in Singapore, can deliver services faster, cheaper and with less friction than traditional banks.
Using these non-standard providers for payment services can give companies an edge by increasing payment options.
Application programming interfaces (APIs) have become one of the most efficient ways to incorporate new technology into an existing ecosystem. They enable companies to quickly expand service offerings, fast-track delivery, improve customer engagement, and drive new revenue opportunities. This is particularly helpful for organisations struggling with legacy systems.
What the Future Holds
No organisation can afford to ignore the payments transformation wave. The benefits are too compelling which includes:
- Faster, more accurate payments transactions
- Reduced exposure and lower costs
- More efficient accounts payable
- Better liquidity management to optimise use of working capital
- Wider choice of services for increased customer satisfaction
- Greater insight into customer behaviour
These topics and more are covered in-depth in Accuity‘s new whitepaper Digital Payments: Is This Really Goodbye to Cash? An Analysis of Business and Consumer Trends.
Featured image credit:Business card photo created by jannoon028 – www.freepik.com







