DeFi made its debut in 2019 and achieved huge user growth in blockchain industry. Yet DeFi is still far from being widely accepted and therefore has great development potential. This article intends to help readers get acquainted with DeFi by introducing its concept, status quo and future.

Picture / Public Information
What is DeFi?
1.1 Basic Concepts
DeFi, short for Decentralized Finance, which is also known as Distributed Finance or Open Finance in China, is a financial business environment without any central endorsement body. Investors can clearly see the fund status and track the status. Moreover, DeFi cannot be tampered with due to technical consensus.
We also see some new technical and business features that DeFi brings to the table.
First, the funds of lending and business transaction are placed on a verified smart contract (or address), which effectively implements transparent supervision of the fund pool. Similarly, fund flow records are distributed on a unified, geographically dispersed ledger that can be universally accessed. This is effective in guarding against technical, financial and geographic risk.
Second, DeFi doesn’t need to conduct background checks and due diligence on borrowers / financiers, which is time-consuming and costly in traditional financial industry. Similarly, there is no need for fund provider to know the specific information of counterparties. The pledge of digital assets / Token can automatically trigger settlement and guarantee lending rights.
Third, DeFi runs automatically in contract code through algorithms, adopts artificial intelligence methods to process core financial logic, and collects market data to form high liquidity capital markets and financial service markets. Therefore, DeFi system can create a more transparent and credible, more fair and equitable credit market. Financial interest rate is no longer determined unilaterally by central bank or authoritative financial institutions, but by algorithms, which truly reflects market supply and demand. These algorithms can implement basic financial logic. For example, if fund supply decreases, interest rate will rise to raise loan costs and if fund supply increases, interest rate will drop to make loan cheaper. In traditional finance, there is a huge gap between regions in fund supply and demand. Fund is getting cheaper in developed countries while becomes more expensive in developing countries. With increasing loan demand in developing countries, the price gap will increase.
Besides, the collateral of DeFi is more than cryptocurrency, but all valuable assets. In theory, any valuable asset could be posted to a smart contract and be used as collateral to obtain financing. When an overdue default occurs, the smart contract will automatically transfer ownership.
It’s true that the realization of all these DeFi concepts still have long ways to go. For an example, before we can collateral to obtain finance, a process is needed to be available for the asset to be link to ownership. At present, some DeFi concepts have achieved a proof of concept, we will introduce them later.
1.2 DeFi is the financial extension of blockchain 1.0
Blockchain 1.0 refers to encrypted digital currency applications represented by Bitcoin, which realize the issue, payment and point-to-point circulation of currency through technologies such as distributed ledgers, chain data and consensus algorithm.
Its core concepts include:
- Absolute decentralization
- High transparency operation
- No real-name authentication
Blockchian 1.0 innovatively realizes decentralized issue, anonymous payment (or transfer) and anonymous custody of digital currency based on blockchain technology and the principle of free currency economics. However, it does not realize the issue of financial lending business and financial derivatives business, which is indispensable and essential to the financial market. Despite the analogy between Bitcoin and gold, there is no denying that Bitcoin itself is a kind of electronic currency that is different from traditional currency system, and its original intention is to realize a kind of currency rather than assets in a stable environment. Since Bitcoin is a kind of currency, it can certainly be used in payment, deposit, lending and derivatives financial operations. From this perspective, it is clear that DeFi business focused on cryptocurrencies is the financial / monetary extension of blockchain 1.0. Currently most DeFi is based on mortgage lending and has huge development potential.
DeFi obviously does not violate the blockchain 1.0 in its core essence, decentralization, high transparency and no real name authentication are still its theoretical foundations. This has opened up another pole of financial services that echoes payment and circulation.
1.3 DeFi is a relative concept echoing traditional finance
Traditional finance is built on trust, while DeFi is built on technical code. Throughout the history of human financial development, trust is the core. The lending relationship between people was built on trust at the very beginning. Lending relationship first occurs only between acquaintances, then between indirect acquaintances. Subsequently, professional institutions such as pawnshop come into being, which gradually play a role in the financial business. After the establishment and popularization of modern company system, such lending relationship gradually occurs between enterprises and individuals, enterprises and enterprises, multiple parties to multiple parties and single party to single party.
However, trust is still the premise of lending, directly or indirectly. With the popularization of electronic technology and information system, data-based analysis and evaluation of the credit of the subject (company or individual) plays an increasingly important role, but this is only an upgrade of trust evaluation system. After the advent of blockchain technology, Defi breaks the conventional wisdom. The lending relationship and process become completely transparent. Smart contract code can recognize the triggering rules of default rules and trigger automatic delivery, thereby achieving “zero human intervention” in financial business. In DeFi mainstream digital currency mortgage business, there is actually no traditional credit and trust relationship, but only consensus and rules, codes and procedures. Their objectivity has replaced trust, the foundation of traditional financial business.
DeFi has replaced credit subject. In fact, traditional financial system still depends on strength, stability, authority and credibility of large financial institutions and regulators. The failure or default of large financial institutions’ credit subjects (large banks / governments, etc.) can lead to the collapse of the entire system. In contrast, DeFi financial system depends on the strength of its protocols, cryptography, and smart contracts. Network scale decides the stability of system, the larger the network is, the more stable the system will be. From this perspective, DeFi is an upgraded version of traditional financial system.
DeFi is fundamentally different in the mode of credit assessment of business participants. In traditional financial system, enterprise size is one of the most common credit evaluation indicators. Hard financial indicators block out a large number of customers with actual financial needs. On the other hand, DeFi allows some relatively weak / small participants to participate equally. Some complex financial services rely on third-party rating agencies, these agencies have their advantages, such as being more professional and more comprehensive in collecting data. However, it is unavoidable that rating agencies themselves are centralized institutions, therefore it is impossible to avoid unfair situations such as “manipulation” and “favoritism.” In DeFi, rating and automatic settlement are expected to be based on completely open and fair data. We are not sure how long this process of universal access will take, but we know that at least the trend is clear.
Theoretically, cross-regional restrictions, peer-to-peer lending and peer-to-peer micropayment which are limited in traditional financial system can be solved in DeFi. Decentralized financial encrypted wallet is actually the equivalent of banknote wallet, autonomous control is entirely in the hands of the owner, the only difference is that one is electronic wallet (controlled by public-private key pair) and the other is physical wallet.
1.4 DeFi interprets the direction of new financial system
Defi brings challenges to existing financial system, but it also calls for some deep thinking about existing economic and financial system.
1.4.1 Should intervention be appropriately reduced?
The original intention of official intervention is to promote the development of the entire economic and financial system, but when government / authority intervenes too frequently in financial and economic development, the reality often goes against expectations, and even leads to “financial suppression”. The so-called financial suppression refers to government’s excessive intervention in financial activities and system that inhibits the development of financial system, financial system lags behind and then hinders economic development, leading to a vicious circle of financial repression and economic backwardness.
This phenomenon is not uncommon. There are lots of human intervention methods in existing financial system, such as financial policies and financial instruments including interest rates and exchange rates.
In fact, economic development is the premise and foundation of financial development, and financial development should only be an auxiliary power and tool for economic development. Obviously, excessive intervention brings no good to financial development, but indirectly brings a negative inhibitory effect on the economy.
DeFi financial system, like Bitcoin encrypted digital currency, is in a non-intervention state. Although it develops too fast to be accepted and it cannot be updated quickly in the short term, it points out a clear direction. DeFi tells us that maybe the new financial system should have less human intervention and more rule-based autonomy, and adapt financial instruments to the market, not the other way around.
1.4.2 Should financial business granularity be finer?
For various reasons, traditional financial services have a coarse granularity of business services. Financial institutions, such as banks, generally value large customers and large fund businesses, while ignoring small, medium and micro customers. The reasons include the preference of executive agencies and the restrictions of macro-policies. For bank clerks in charge of lending business, they prefer large and reputable enterprises such as central enterprises and state-owned enterprises. Those enterprises have large amount transactions, strong risk control capabilities, yet its operation cost is no higher than smaller customers, therefore clerks cannot be motivated to serve smaller customers. Another example, policies stipulate a threshold for a qualified investor, this is to protect small and micro investors. This will undoubtedly block out many small and micro investors with financial needs but limited assets.
From this point of view, the granularity of financial services is still not fine enough at both Business end and Consumer end. As a result, small Business and small Consumer cannot enjoy the same financial services and rights. With the increasing awareness of civil rights, financial services rights will become increasingly important, and this trend is irreversible.
At the national level, one of the real problems in providing better services for small, medium and micro enterprises may be the granularity of financial business services.
In DeFi, financial services granularity can be fine enough that people can invest even $1.00 or less, and the corresponding small asset holder can theoretically borrow the same amount of funds that he holds.
1.5 Mainstream form of DeFi
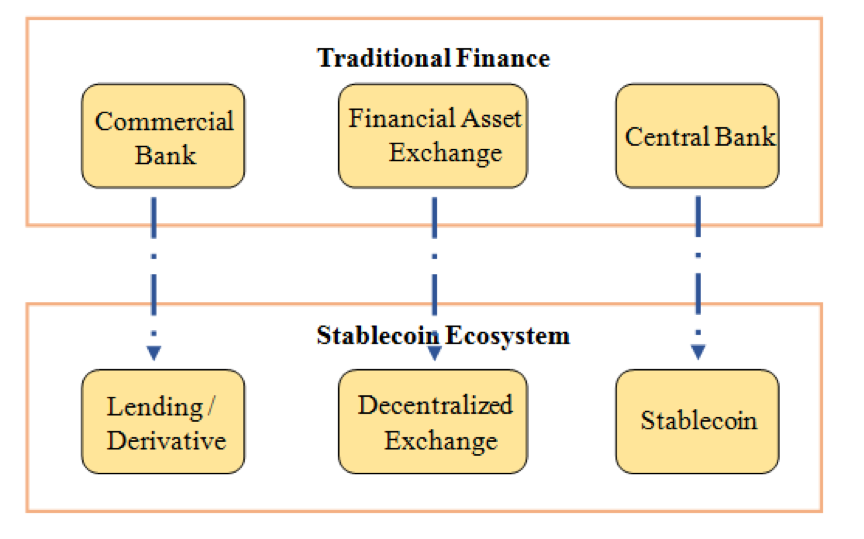
DeFi mainly includes decentralized lending, decentralized exchanges, stablecoins (payments / assets), and other decentralized derivatives. From a traditional financial perspective, lending business and derivatives actually play the role of commercial bank; decentralized exchange plays the role of stock exchange / financial asset exchange; and stablecoin business is much like a business of traditional central bank.
Picture / Public Information
1.5.1 Mortgage lending
Decentralized lending is an attempt to free financial services from relying on centralized institutions and to achieve a highly fair and transparent financial lending relationship. Fundamentally, it is a type of decentralized application. At present, mortgage lending is still the main form of DeFi lending. Mortgage lending makes up for some of the shortcomings of traditional finance, for example, investment limit can be set without a lower limit, funding provider requirement is less stringent, the entire business process is more open, the boundaries are clearer, and centralized supply and demand matching is provided.
We can make a brief analysis of MakerDAO, the “Financial Leader” of DeFi and the most well-known project on Ethereum, to understand the principle and logic of lending business in the decentralized world.

Picture / Public Information
- Release media. By playing the role of traditional central bank, MakerDAO has issued stablecoin DAI, and anchored it to the US dollar at 1:1, so that there is a unified exchange medium. MakerDAO actually acts as a bank in the decentralized world.
- User application. When a user needs to borrow money, MakerDAO doesn’t check the user’s credit history like what traditional finance does. In fact, DeFi also cannot check offline credit because user information in application record as it is only an address. Therefore, MakerDAO will let users mortgage blockchain assets, such as the most commonly used ETH (Ethereum Token). If the user has ETH worth US $ 150,000 (estimated based on the current market price), user can mortgage it to MakerDAO through smart contracts. MakerDAO will give user up to 100,000 DAI (worth US $ 100,000) because Maker DAO stipulates that the value of the collateral is at least 1.5 times the lending amount.Mandatory redemption. If the market declines after user borrowing the money, the value of user’s mortgage of 150,000 US dollars will also fall. If collateral value is close to DAI ($100,000), MakerDAO will force the sale of user’s ETH to repay his loan. This is also a “self-protection” measure in DeFi business. These conditions are all triggered by smart contracts and can be monitored by users.
- Contract lending. The platform lends money to users through DAI. After holding DAI, users can freely exchange, circulate and use it.
- User repayment. when users repay, they must also obtain DAI through exchange, circulation or other methods, then return DAI to MakerDAO and pay interest to redeem the previously mortgaged ETH assets.
1.5.2 Decentralized exchange
Decentralized exchanges allow users to trade digital assets such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Decentralized exchanges are created to solve the problems of artificial manipulation in centralized exchanges.
In centralized exchanges, users do not own their own private keys, so they cannot control their own property. In decentralized exchange, there are issues with efficiency. A hybrid of exchange modes concerning these two propositions have been generated.
They are not quite the same, I will briefly introduce the principle from two commonly used modes.
On-chain orderbook mode
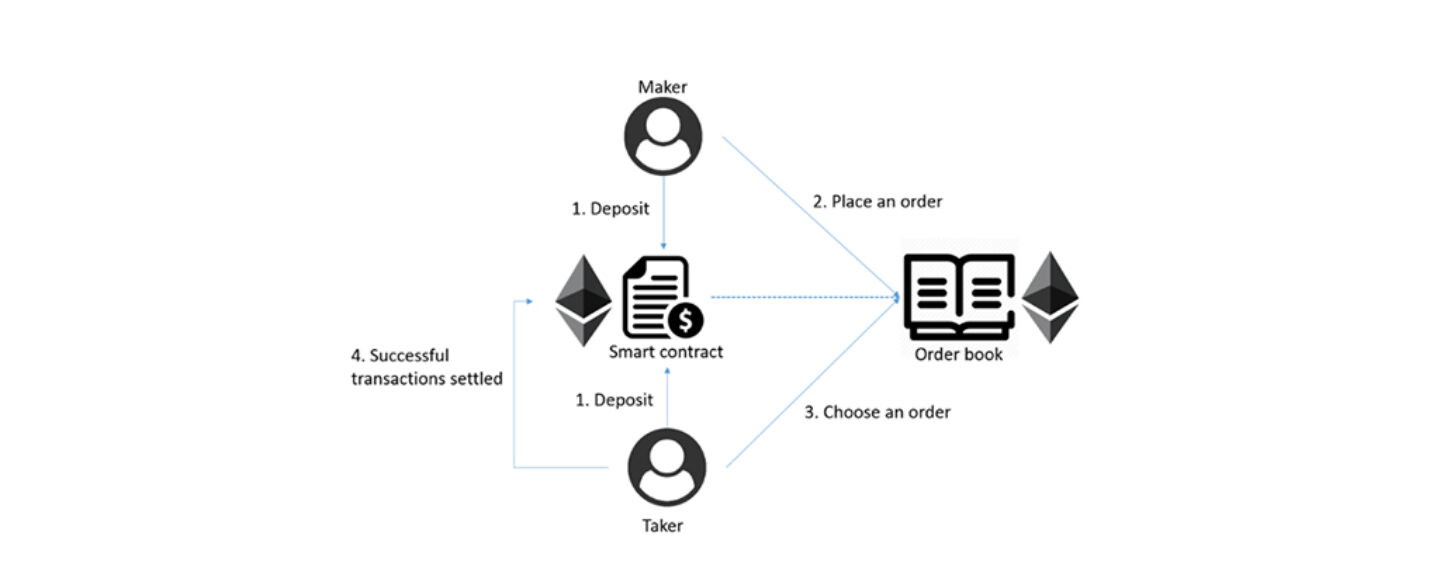
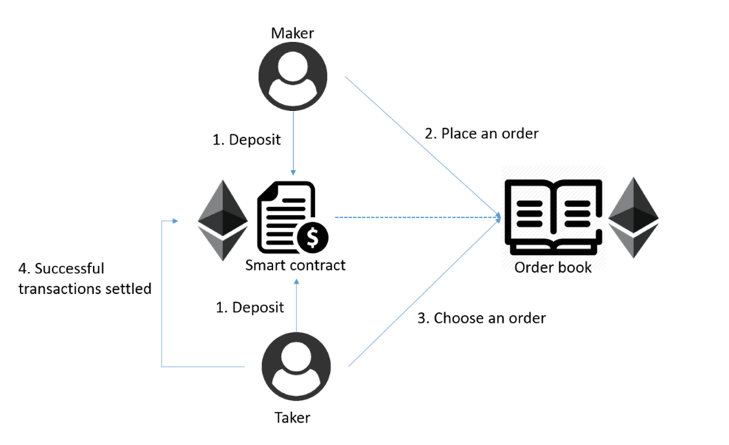
This is the most classic and a relatively decentralized mode, in which user recharge, maker, taker, settlement and withdrawal are all completed on the chain. The decentralized exchange Etherdelta is a representative of this mode.
A brief process is described as follows:
Picture / DExtop_official
- Maker and Taker recharge assets into smart contracts, user assets are managed by smart contracts, and contract administrators cannot arbitrarily manipulate user assets.
- Maker places an order on blockchain (usually public chain).
- Taker selects the order that he wants to trade and initiates a transaction.
- The smart contract will match the needs of Maker and Taker, and transaction will be settled on the chain.
Offline orderbook mode
This mode takes into account both the security of decentralized exchange and the efficiency of centralized off-chain matching mechanism. At present, the Ethereum decentralized exchange IDEX is the representative of this mode.
A brief process is described as follows:
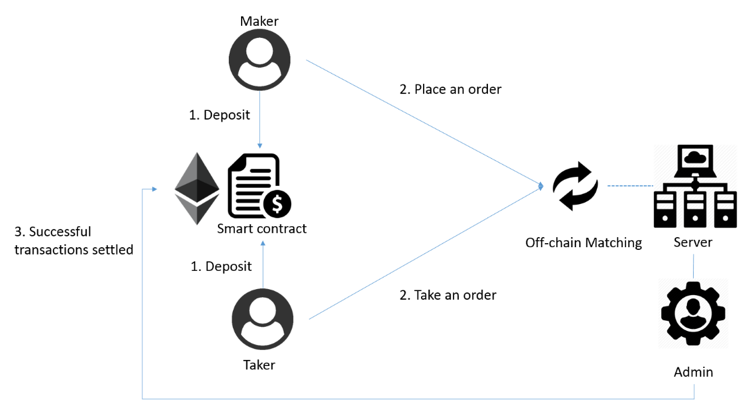
Picture / DExtop_official
- User recharges digital assets into platform’s smart contract through private key signature authorization; the platform does not have access to user’s private key and assets for security issues.
- Off-chain server processes user’s maker and taker operation, which ensures that the transaction experience is basically consistent with that of centralized exchange; uncompleted maker will not cause loss of gas costs and save the cost of on-chain invalid orders.
- Ledger synchronization: ledger processed by off-chain server and successfully matched result information will be sent to on-chain ledger, and finally store transaction information on the chain.
1.5.3. Stablecoin
Payment media are the prerequisites for DeFi business. The value of digital currencies fluctuates greatly, while fiat currencies face various regulatory and policy issues, and are not suitable as payment tools in DeFi field. Therefore, stablecoin is the best choice for DeFi.
Stablecoin is the product of digital currency transactions. Fiat currency cannot directly serve as pricing unit due to various reasons, but in reality, the popularization of digital currency including DeFi business cannot be separated from fiat currency pricing. So, it is important to possess digital assets with stable price. Transaction media, bookkeeping units and value storage all need such kind of currency with blockchain attributes. Stablecoin is a blockchain-linked currency with stable price, it bridges the gap between fiat currency and digital currency.
For example, MakerDAO has issued DAI stablecoin for DeFi business settlement and transactions. Libra, which is scheduled to be launched in 2020, is a typical stablecoin, and its volume is also considerable. The essence of Libra is a stablecoin issued by bind assets which consist of a package of fiat currencies (multiple countries) to carry out related business in different countries / regions.
Therefore we see that stablecoin also has different modes, and three main modes are as follows:
- Fiat currency asset mortgage mode. It is bound in a single fiat currency (such as US dollar) or multiple currencies and is usually issued at 1:1 ratio. Other assets with stable value attributes, such as gold, also fall into the category of mortgages. The stablecoin under this mode is the one with the best stability, but it has a fatal problem in preventing “false issue”. USDT is a good example.
- Digital asset mortgage mode. It uses a single digital asset currency or multiple digital asset currencies as the anchor asset. The biggest uncertainty of this mode is the fluctuation of digital asset value, and the risk of failure.
- Algorithm mode. Currency value is calculated through market asset comprehensive automatic assessment. This mode is the most complex one, yet it is the most independent, with no reliance on external credit at all.
The stablecoin itself also has business profit modes such as exchange rates and holding income. Once it is popularized and gains public consensus, its business scale will be unlimited, for instance, USDT, the pioneer of stablecoin.
Besides, there are currently thousands of DeFi projects. In addition to the above three mainstream modes, there are also decentralized wallets, insurance platforms, identity authentication, KYC / AML, market analysis, quantitative transactions, and so on. These modes are not that typical, so this article will not have further discussion.
2. Development Status
2.1. Overview of DeFi market development
2.1.1. Lending business
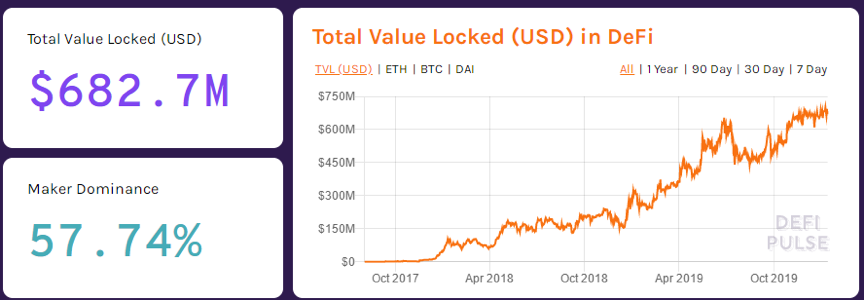
We can also see the trend of ETH-based DeFi financial business locked position from DEFI PULSE:
Data / DEFI PULSE
The three major platforms, Maker, Synthetix and Compound are in a leading position, especially Maker, which until now (January 2020) still occupies half of the market shares. Total locked market value is worth up to US $ 682 million (data statistics as of January 12, 2020).
Back to the beginning of 2019, MakerDAO led the DeFi trend, almost dominating the DeFi market in terms of user number, locked value, and business mode. After one year of development, DeFi market becomes more competitive, more and more people participate in this emerging market. The anchor currency has also evolved from ETH to ETH, DAI, and EOS.
【DAI is a stable digital currency derived from MakerDAO project in accordance with market mechanisms, and DAI/USD keeps 1/1. Maker is one of the earliest decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO) and smart contract systems on Ethereum platform. The Maker platform provides stable basic currency DAI. Thus, DAI is regarded as one of the basic currencies secured by digital assets. If you’re interested in it, find more details at https://makerdao.com】
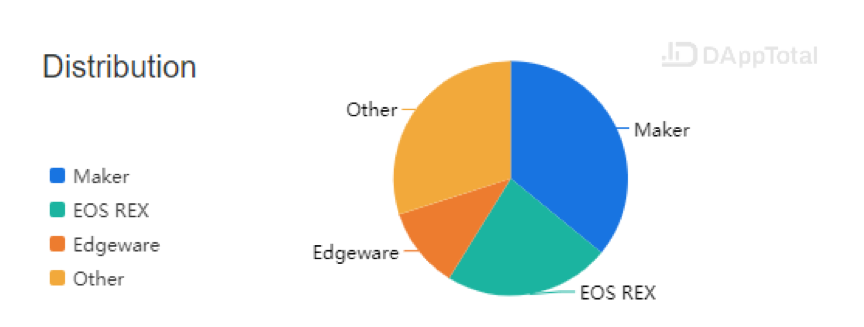
As of now (2020-01-12), total value locked in DeFi market has reached US $ 928.07 million. Maker, EOS REX and Edgeware account for more than 70% of the total.
Data / DAppTotal
It is not difficult to find from locked value trend that the past year is DeFi’s fastest-growing year.
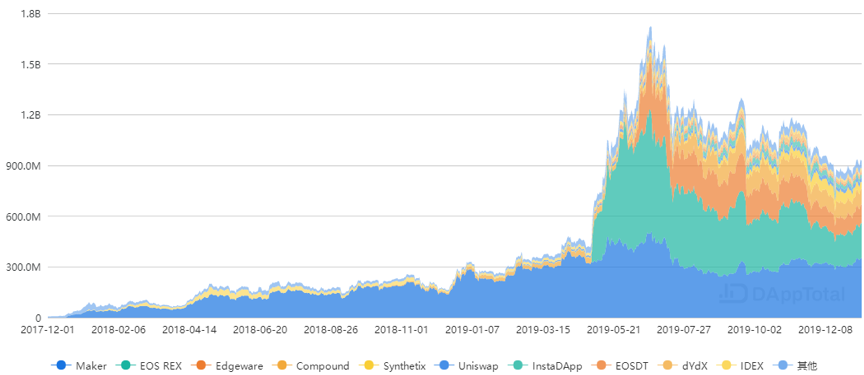
Data / DAppTotal
It is not difficult to find that after 19 years of development, DeFi is no longer the sole market of Maker, and ETH is no longer the only currency. DeFi ecosystem has basically formed a new situation of multi-subject competition.
From the perspective of the project, Nuo Network, a lending platform on Ethereum, and derivative platform Augur and Bancor all perform well and are worthy of attention; but a few, such as Veil, fail to survive.
Fortunately, in addition to ETH and EOS ecosystem, Layer-2 Lightning Network, a Bitcoin-related project, also expands DeFi business through massive nodes. The locked value in the network climbs to 862.56 Bitcoins, which is about US $ 6.25 million.
2.1.2. Decentralized Exchange
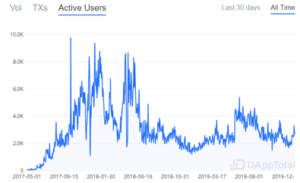
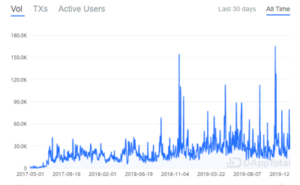
Decentralized exchange is currently dominated by Uniswap, accounting for more than half of the transaction volume, followed by DDEX, ETH2dai, and IDEX.
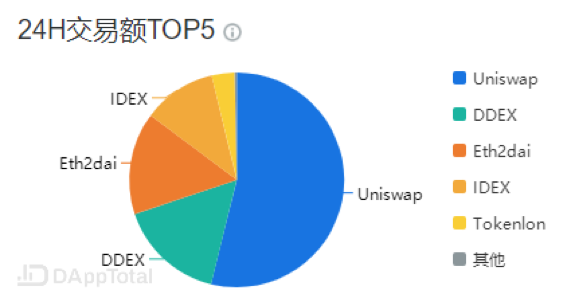
Data / DApp Total
Here are the transaction and user statistics from DApp Total:
- Data / DApp Total
It is not difficult to see that the development of DEX cannot be separated from the development of overall macro currency market environment, and bear market users and transaction volume have decreased significantly; but the daily transaction volume still exceeds 20,000 ETH per day, which cannot be underestimated; At present, no more than 3,000 users join the market every day, therefore, it is still a niche market.
2.1.3. Stablecoin
At present, the total value of stablecoin market is as high as US $ 5.7 billion, of which USDT accounts for about 83%, and it is an absolute leader in stablecoin market. (Data as of 2020-01-12)
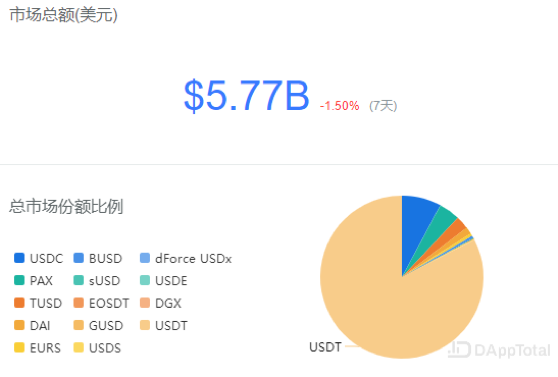
Data / DApp Total
According to DAppTotal, DAI accounts for about 8% of the market share of emerging currency market.
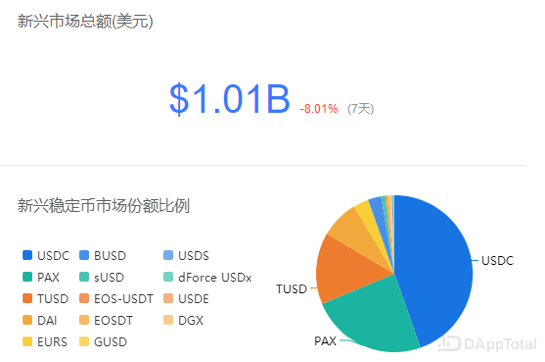
Data / DApp Total
In 2020, Libra is estimated to be the biggest shock to stablecoin market. Libra is expected to go online in the first half of 2020. Once launched, it will certainly seize some of the original stablecoin market shares.
Judging from the financing situation of the entire DeFi ecosystem, the total scale of financing in the past year (2019) has exceeded US $ 70 million, most of which focus on lending business. Participating parties include top venture capital firms such as Sequoia and they are mainly based in America, with more than 60% of investment funds coming from US funds and VCs, such as a16z, CoinbaseVentures, Polychain, Paradigm, etc. Among them, MakerDAO has raised over US $ 27.5 million in two rounds of financing. Compound also performs well, ranking second with a financing amount of US $ 25 million. ACINQ, one of the Lightning Network development teams, also successfully raised up to US $ 8 million.
In general, DeFi business mode has been verified and promoted to a certain scale in 2019, and the product ecosystem is also growing. What’s more, follow-up projects such as public chains (Polkadot) and traditional mainstream currencies (such as Bitcoin) will be gradually integrated into DeFi ecosystem. 2020 will be a year worth looking forward to.
2.2. Development bottlenecks and fields to break through
2.2.1. Cognitive threshold
Compared with traditional financial service institutions, DeFi does have many advantages, such as decentralization, high transparency, low fees, etc., but its current popularity rate still has much room for improvement. DeFi is strongly related to blockchain technology. Defi is currently like the blockchain technology in mid-2016, only a minority of people are aware of it. The reason for this is largely determined by technical threshold. Many people do not even understand blockchain technology, let alone Defi, a subset of blockchain with relatively high cognitive threshold and technical and business complexity. To put it another way, DeFi’s current innovative products have not reached the level of general participation of ordinary people and investors. Most ordinary investors focus on whether the product is profitable and the proportion of profits, rather than on technological innovation.
On the other hand, DeFi practitioners’ cognition also has room for improvement. As DeFi is still a technology-driven emerging industry, practitioners are still subject to technical personnel. Generally, these technical personnel are good at technology and blockchain, but still have ways to go in understanding financial services, especially compliance and other related fields.
2.2.2. Performance bottleneck
【Public network performance restrictions】
Lending business itself is carried out on its own chains (currently on Ethereum and EOS). ETH only has one block every 15S, and the main network TPS does not exceed 100. This is a huge gap for financial business systems. If 10,000 users are concurrent, then the performance gap is 100 times greater. In fact, in China’s domestic centralized trading exchanges, it is very common to have more than 10,000 concurrent Consumer end users.
Decentralized exchange product experience also has a direct dependence on main network, so we see that there are two basic categories: “on-chain mode” and “off-chain mode”. In theory, the on-chain mode is the real decentralized transaction. Users manage their private keys, the platform does not have access to users’ assets. The entire process is safe and transparent. The core of exchanges is to play the function of transaction matching. Centralized transaction itself also requires a certain transaction depth to help improve liquidity. Therefore, this means high-frequency operations are required, each maker, cancellation and transaction operations are all triggered by smart contract or happened on the chain, which is undoubtedly a great test for DeFi practitioners and related institutions.
【Product experience issue】
Blockchain confirmation requires the participation of several blocks. As a result, there will be asynchronous confirmation of business operations, users will not get immediate response. Yet the results of centralized applications will be given without delay, therefore bring some problems to decentralized applications and decentralized finance at the basic level and need for further development.
At present, several decentralized exchanges and lending DAPP on the market are not that user-friendly and are complex to operate. This will have a fatal impact on financial applications, especially on inclusive finance, as most people may give up using because of the high cognition threshold.
【Transaction cost issue】
Since each business operation is submitted to public network for verification, there also exists a Gas cost problem, that is, in addition to the traditional fee for each financial business, another Gas cost will be incurred through at least one (usually multiple) blockchain confirmation process and increases transaction cost. It seems that the cost of a single transaction does not increase much, but when this cost is multiplied by the transaction volume, it will be too high to be affordable.
Based on this, in order to solve the problems of high cost and low efficiency of complete on-chain transactions, the industry has also pioneered the development of fund pool mode and off-chain mode, in exchange for part of product experience at the cost of losing independence, but it still falls short of the requirement of universal application.
The performance of blockchain micro-technology is still a subject to be studied continuously.
2.2.3. Fund efficiency
From the perspective of financial business, fund utilization rate in DeFi’s current lending business is not high. Due to the platform’s risk control requirements, the value of required mortgage assets must be higher than the financing amount, otherwise zero risk cannot be achieved. For example, the MakerDAO mentioned above requires users to deposit 1.5 times the ETH price to establish a mortgage debt warehouse that supports DAI. Moreover, some platforms require 2 times and 3 times the mortgage assets, which undoubtedly greatly reduces the efficiency of fund asset utilization.
In contrast, traditional financial mortgage evaluation is more effective, and in addition to mortgage loan, there are many types of credit products that do not require collateral, such as credit loan.
In terms of improving the efficiency of fund utilization and the design of financial products, DeFi still has a lot of room for development.
2.2.4. Systemic risk
【System associated risk】
DeFi projects can be nested with each other. In terms of ETH DeFi ecosystem, MakerDAO plays a similar role as “central bank”. The adjustment of its strategy will directly affect the operation status of secondary lending products such as Compound. Compound, Uniswap and other secondary DeFi products have enriched the product types of ETH DeFi ecosystem and are beneficial to the entire ecological development, but they are too closely linked, the entire ETH DeFi system is more likely to crash when a single product or protocol being attacked.
In addition, it should be noted that there exists homogeneity in DeFi’s own business products. Mortgage assets may have a “long” effect. At present, there is no complete post-lending detection technology to eliminate the risk of multi-purpose mortgage assets.
At present, DeFi post-lending management is not as good as traditional finance, as fund usage is not tracked. I learn that a wide range of DeFi users borrow money mainly for coin stock, that is, to go back and invest in mortgage currencies. For example, ETH holders borrow stablecoin DAI by pledging ETH, and then reinvest, buy and hold ETH via DAI exchange, creating a leverage amplification effect.
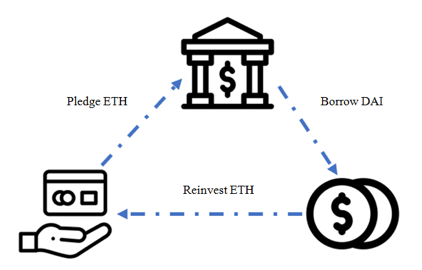
Users of course benefit when the current market goes up. Once market goes down, however, users will lose their money. When exchange scale is enlarged, it is very likely to bring lots of users financial losses that beyond their risk tolerance, resulting in sever consequences and huge impacts.
3. Future Directions
Judging from the development of blockchain and related ecology in recent years, finance and gaming are the first two industries that implement blockchain technology and have the most relevant DAPPs. However, the current gaming industry is actually not successful, and its future is not that bright. At present, some of the more active gaming industry are those with financial attributes, and some even have the risk of breaking the law. So, the key lies in financial field. After a year of development, DeFi is very likely to witness explosive growth in 2020. In general, several points of DeFi’s future development are worthy of concern.
3.1. Subject to supervision
Supervision is an unavoidable topic for financial industry, financial business and DeFi is no exception. Financial innovators tend to underestimate the value of existing systems and supervision mechanisms. It is important to know that existing business modes and supervision policies are shaped by economic and political environment. In blockchain industry, both systems and systems are the object of criticism, but from the perspective of technological and social changes, when innovation is in growth stage or transition period, it is often necessary to follow the existing system first, then break it, and promote changes in policies and systems. Faster innovation and greater span often bring greater resistance. Even Libra, which is directly promoted by the globally recognized Internet giant Facebook, may be in trouble right now. In Mark Zuckerberg’s recent speech about Facebook’s 10-year vision, he did not mention Libra, and this is perhaps the best illustration of the current supervision dilemma.
Theoretically, a trusted distributed computing network allows DeFi to build financial services on a globally auditable digital ledger, and the business logic is automatically executed on the contract code to the greatest extent. These features can improve the level of automatic risk management and supervision capacity, which is extremely beneficial to the development of global financial business. Cross-border risk control capabilities and consensus rules can better integrate financial services across regions, and promote more efficient, transparent and flexible financial systems, and this is the essence of DeFi.
Specifically, taking China as an example, DeFi currently needs to be consistent with the blockchain empowerment advocated by the policy, drives business innovation with technological innovation, and empowers financial institutions and small and medium-sized enterprises. At present, domestic cross-border e-commerce, cross-border logistics, and multilateral trade all need this technology to drive the development of innovative financial modes and empower the entire social and economic development.
3.2. Closer integration with traditional finance
If DeFi needs to develop on a larger scale, it will inevitably need to further integrate with traditional finance.
In addition to machine learning and artificial intelligence, FinTech (financial technology), which is currently popular, has already embraced blockchain technology to help strengthen trust in traditional financial systems, improve data quality and make better risk prediction and judgment.
The core of FinTech is creditability. DeFi can be considered to have no creditability (no offline review), or 100% creditability (completely based on mortgage). DeFi hopes that all assets can be tokenized to form the basis of DeFi mortgage lending. This is fully consistent with the current trend / policy of traditional finance and policies. At present, the government is advocating the digitalization of assets and the authentication transaction of digital assets. After the assets being digitized, they can theoretically be traded and circulated globally. Therefore, digital assets and DeFi are similar in many places, the only difference lies in the way of networking (alliance chain VS public chain). How to integrate the two is an important issue facing the industry.
Take mortgage loan as an example, under the current scheme of alliance chain, traditional asset evaluation is put on the chain to increase credit, and then goes online and offline. However, if we lift regional restrictions and do cross-border capital asset docking (such as inflow of foreign fund), then it will theoretically be a DeFi form that is compliant and fully integrated with traditional financial services.
In addition, the DCEP (Digital Currency Electronic Payment) issued by the People’s Bank of China is expected to be launched in 2020. Experts predict that DCEP may partially replace cash, which is likely to become a bridge between DeFi and traditional financial services and accelerate the integration of DeFi and traditional financial services.
3.3. DeFi currency will be diversified
3.3.1. BTC
At present, DeFi ecological anchoring asset is still dominated by ETH, while assets like Bitcoin that actually has both currency / gold attributes have not been widely adopted. This is a gold mine that has been forgotten by DeFi. Bitcoin is fully qualified as a collateral in terms of recognized value, liquidity, asset size, etc., and it is even better than ETH and EOS in terms of value stability. Some countries have already qualified Bitcoin as asset rather than security, which is more acceptable at regulatory level.
At present, BTC’s DeFi only has some simple attempts, such as packaging BTC into imBTC and xBTC in ERC20 format, and DeFi platform Money on Chain, which imitates MakerDao mode and is based on Bitcoin sidechain RSK. There will probably be more DeFi projects focused on BTC.
3.3.2. Libra
Libra is expected to be launched in 2020. It is promoted by the global Internet giant Facebook and is dedicated to making banking services available to people without bank accounts. Libra is an encrypted digital currency that does not pursue stability against the exchange rate of the US dollar but pursues relatively stable actual purchasing power. As Libra naturally has more than 2 billion Facebook users, it will undoubtedly have a great impact on world-wide financial landscape. I believe that Libra will not be overlooked in DeFi field.
Although there are still some uncertainties about Libra, it is undeniable that the mode and trend it brings are inevitable. Once Libra goes online and is accepted by influential countries / regions, Internet finance industry will meet great changes, and DeFi will be combined with Libra to form a global financial instrument market, which will rapidly promote a more balanced supply and demand of funds.
In addition to new stablecoins like Libra, there are existing stablecoins, such as USDT, and some DeFi lending projects have begun to talk about USDT, but in general, from my point of view, USDT has been discredited due to issuance and will gradually go downhill and will not have a decisive impact.
In conclusion:
DeFi makes finance more democratic, transparent and fair!
DeFi is building new financial system!
DeFi is leading the future of finance!