In 2024, the banking sector is witnessing a pivotal transformation driven by advanced technologies like AI and cloud computing, evolving customer demands, and changing regulatory landscapes.
This evolution reflects the dynamic shift seen a quarter century ago with the Digital Age, challenging the traditional banking model and echoing Bill Gates’ famous words, “The world needs banking, but it does not need banks.”
Accenture’s “Top Banking Trends 2024” report for this year highlights this transformative journey. It outlines the top banking trends, such as the adoption of generative AI, offering both challenges and opportunities.
To stay relevant, banks must embrace these trends, reinventing their operations and business models to deliver innovative, customer-centric services.
In this rapidly changing environment, adaptability is crucial for success. Banks that can agilely respond to the top banking trends and discern the noise will probably emerge as leaders, defining the future of banking in an era increasingly shaped by technological advancements.
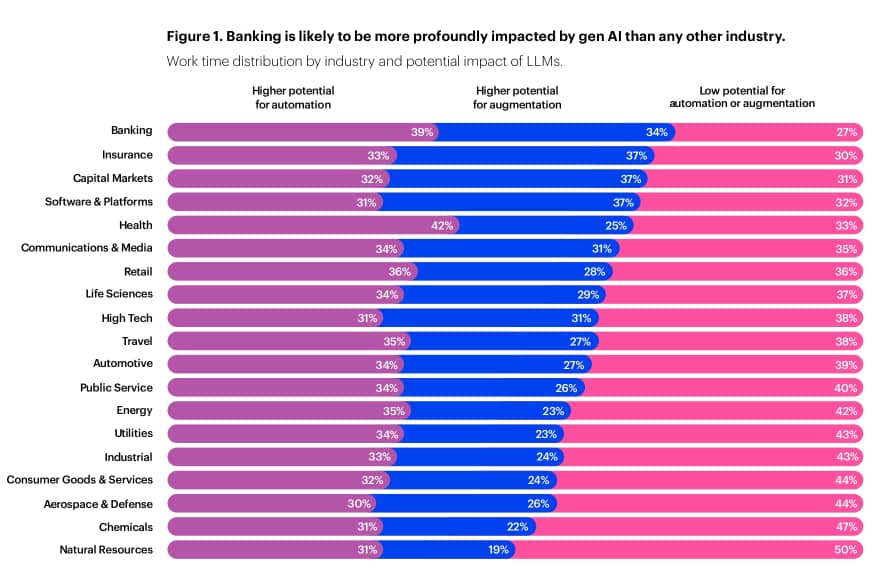
Generative AI supercharges banking.
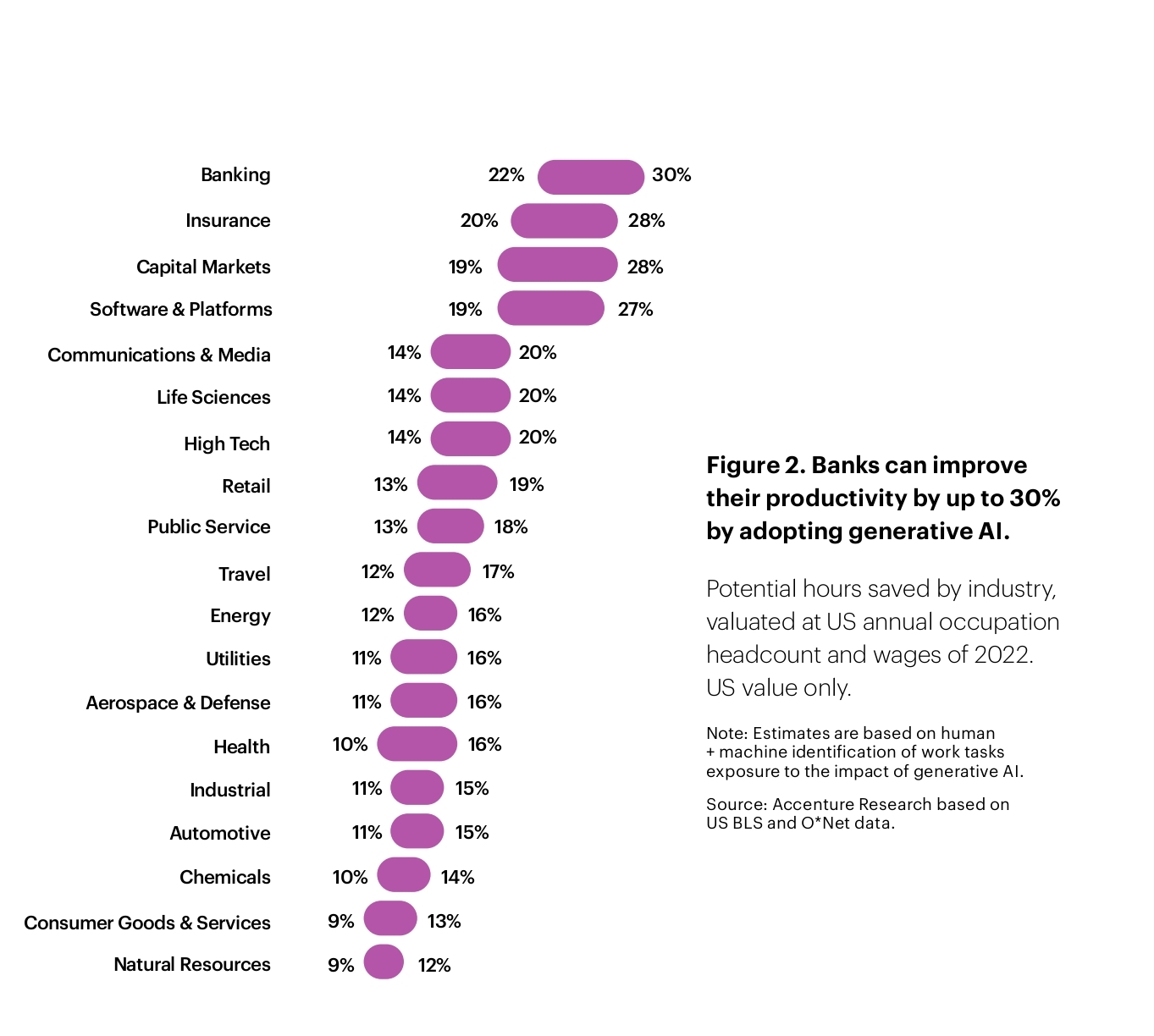
Generative AI will provide the banking industry with unparalleled advantages. Operational efficiency analysis suggests the potential to boost productivity by 22-30 percent, and studies show that revenue could increase by 6 percent.
To realise these gains, banks must effectively leverage the cloud and data and, crucially, rethink their approach to work and talent.
Within a year of its launch, ChatGPT and generative AI found widespread adoption within the banking sector. Banks are now implementing generative AI strategies and reporting impressive results.
Generative AI offers many applications in banking, from enhancing due diligence and risk management to streamlining legal contract generation and code writing.
However, its most significant financial impact will be improving sales and marketing efforts, quality of customer interaction, and product application processes.
Beyond sales and marketing, other functions like risk management, compliance, technology, human resources, and legal will also receive attention as generative AI reshapes banking.
Capturing the digital dividend with AI
While banks have made substantial progress in digitalisation, the focus has often centred on servicing rather than fostering meaningful customer interactions.
AI holds the potential to unlock the true value of digital channels, enabling banks to have substantive conversations with customers across digital platforms.
In 2022, data showed that bank customers still frequently utilised branches for various services. However, only a small percentage of banks offered comprehensive rewards for customers who increased their engagement with the bank.
In 2024, a growing number of banks will leverage customer data, advanced analytics, and AI to move beyond basic demographic segmentation, adopting a “lifecentric” approach.
This strategy encourages customer loyalty and enables banks to engage with customers proactively, offering tailored advice and relevant offers.
Unseen risks in the banking sector
In 2024, banks face various familiar risks and less predictable risks. These include cybersecurity threats fuelled by generative AI, high mortgage rates and inflation challenges, and potential commercial real estate market disruptions. Banks must proactively plan and adapt to mitigate these risks effectively.
While banks have invested heavily in cybersecurity, generative AI has introduced new vulnerabilities, such as deep fakes and sophisticated phishing attacks.
Banks will need to shift their strategies from prevention to resilience, using AI to detect attacks and enhance scenario planning and response.
High mortgage rates and inflation pose a risk of stressed customers defaulting on their mortgages, potentially causing government interventions. Banks must assess their readiness to address interest rate-related risks and potential economic challenges.
The commercial real estate market also faces uncertainty because of shifting work patterns and economic conditions. Banks, insurance companies, and pension funds must prepare for and carefully monitor this risk.
Additionally, the rise in shadow banking poses questions about the true extent of risk in the financial system.
Banks hold less than 50 percent of financial assets, and the share of non-bank mortgage origination has surged. Monitoring and addressing this risk are essential for stabilising banks, insurance companies, and pension funds.
China’s growing involvement in global economies and risks in its residential property sector demands scrutiny. Despite regulatory efforts, the high leverage in this sector and the potential bubble could have severe repercussions for global banks and economies if not adequately addressed.
A new era of the banking workforce
Banks are on the brink of a radical shift in their workforce dynamics, aligning with the top trends in banking. As AI and generative technologies become integral to banking operations, new skills, mindsets, and approaches will be essential.
Unlike previous shifts, this transformation goes beyond recruitment; it requires a fundamental reimagining of banking professionals’ work.
Competition for technical talent will intensify in 2024 as every financial institution aims to capitalise on AI, cloud, and data analytics.
While some banks invest heavily in their IT organisations, the demand for expertise will likely outstrip supply. The most talented individuals will seek career paths leading to leadership roles.
Singapore’s OCBC Bank provides an example of this transformation. It recently completed a successful six-month trial of an intelligent chatbot, now rolled out to its 30,000 employees. This chatbot speeds up tasks like writing, translating, researching, and innovating, with participants reporting 50 percent faster work completion, including verification.
A previous trial boosted productivity in areas like code development and document summarisation.
The bank employs AI for over four million daily decisions in risk management, customer service, and sales and expects to reach 10 million by 2025.
Optimising pricing with AI
In 2024, one of the top trends in banking is the industry’s focus on optimised pricing, recognising its significant impact on their bottom lines.
Banks are taking a new approach by combining intuition with generative AI and comprehensive data to enhance scenario planning and move closer to personalised pricing.
A 1 percent increase in revenue translates to a significant improvement in pre-tax ROE for banks, making pricing optimisation crucial. Traditionally, banks struggled to accurately predict the impact of price changes on revenue.
AI will enable banks to consider thousands of variables rapidly, determining the ideal price for each customer, product, and channel.
Embracing a cloud-first approach
The banking industry’s adoption of cloud technology is one of the top banking trends in 2024. This marks a significant change in how banks operate and utilise technology. Banks are recognising the potential of cloud technology to leverage data, generative AI, and emerging technologies.
Consequently, they are moving away from traditional on-premise models and embracing a more dynamic, cloud-centric framework. This transition necessitates comprehensively reevaluating processes, architecture, skills, and corporate culture.
Previously, cloud adoption was primarily IT-driven, but now, it’s increasingly led by business leaders who see the cloud as more than just a data storage solution. It represents a new way of working, demanding flexibility, agility, and openness to innovation.
Regulation recalibrated
The banking industry has grappled with an ever-expanding volume of regulations since the 2008/2009 Financial Crisis.
However, many of these regulations have not directly addressed the root causes of bank failures. In 2024, we expect increased collaboration between banks, central banks, and regulators to develop more effective regulatory approaches.
While the regulatory landscape has expanded significantly, it has not addressed the key factors leading to banking failures, such as credit risk and liquidity.
The compliance burden on banks has grown substantially, with rising operating costs, as new regulations continue to emerge.
Shifting from technology management to engineering
A subtle yet profound shift is occurring in leading banks—transitioning from a technology management mindset to an engineering approach.
Banks recognise the importance of building with technology rather than simply managing it. This shift encompasses all aspects of banking, from IT to the C-suite.
One of the top trends in banking is this transformation towards adopting an engineering approach.
A case in point is J.P. Morgan, which has embraced this shift by referring to its team of 40,000 computer scientists and technologists as engineers. In both cases, the roles have evolved from mere technology management to active involvement in its design and construction.
While bankers may not typically view themselves as engineers, their shift in focus from maintenance to design and development represents a positive change that holds significant long-term growth potential for the bank.
This shift affects IT and permeates every level and function within the banking sector.
Unlocking the legacy core
For years, banks have grappled with outdated core systems, hindered by millions of lines of COBOL code that are outdated and poorly documented.
Modernising these systems has been daunting, often requiring years and significant financial investment.
However, generative AI is now emerging as a game-changer. It can reverse-engineer and untangle COBOL code, making it easier and faster to modernise legacy systems.
This technology can significantly reduce costs, minimise disruptions, and enhance regulatory compliance.
Beyond Six Sigma – creative cost reduction
Banks have long sought ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency, often through methodologies like Six Sigma. However, in 2024, there’s a shift towards a more creative approach to cost reduction.
Banks are reimagining their operations, products, and customer experiences. They are leveraging generative AI to enhance productivity and reshape the business.
Banks are combining classic Six Sigma rigour with design-led thinking and AI-powered tools, positioning themselves to tackle old challenges in new ways.
This approach allows them to achieve short-term efficiencies and long-term value for customers and shareholders.
Banking’s transformation in 2024
Generative AI stands at the forefront of the banking industry’s transformation, offering a disruptive potential that promises to usher in a new era of enterprise intelligence.
According to Accenture’s Technology Vision study, 95 percent of C-level executives foresee advances in generative AI delivering positive returns on AI initiatives.
2024 will be a pivotal moment for the banking sector, with generative AI driving the top 10 trends that will reshape the industry.
Banks that adeptly harness this technology and adopt strategic approaches will emerge as leaders in the modern banking landscape, marking 2024 as a year of remarkable progress and transformation.
Featured image credit: Edited from Freepik